CPF Contribution Rate
CPF Contribution Rate
Blog Article
Title: **Navigating Financial Security: A Comprehensive Guide to CPF Contribution Rates in Singapore**
Introduction:
In the vibrant economic landscape of Singapore, financial planning and security are paramount. Central to this is the Central Provident Fund (CPF), a comprehensive social security system that plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the financial well-being of Singaporeans. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the CPF contribution rates, shedding light on their significance, structure, and implications for individuals and the broader economy.
**Understanding the CPF:**
The Central Provident Fund (CPF) is a comprehensive social security system in Singapore designed to provide financial security for citizens throughout their lives. Established in 1955, the CPF has evolved over the years, encompassing various schemes and accounts that cater to different aspects of an individual's financial journey, including retirement, healthcare, and home ownership.
**CPF Contribution Rates:**
CPF contribution rates represent the percentages of an individual's income that are set aside for contribution to their CPF accounts. These rates are structured to address different financial needs, including retirement savings, healthcare coverage, and housing.
1. **Ordinary Wage (OW) and Additional Wage (AW):**
- CPF contributions are categorized into Ordinary Wage (OW) and Additional Wage (AW). The Ordinary Wage includes an individual's monthly wages, while the Additional Wage encompasses bonuses, overtime pay, and other variable components.
2. **Employee and Employer Contributions:**
- CPF contributions involve both employees and employers. The contribution rates are divided into the employee's share and the employer's share. These rates vary depending on the employee's age and the type of income (OW or AW).
**CPF Contribution Rates by Age:**
The CPF contribution rates are structured to adapt to the changing financial needs of individuals at different stages of their lives.
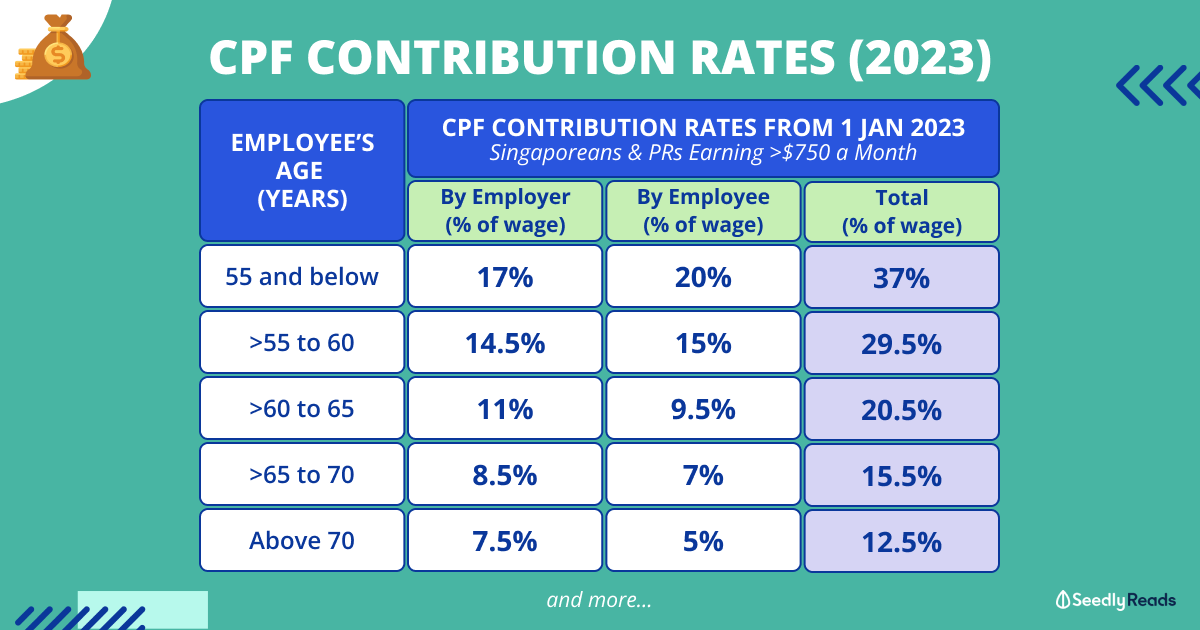
1. **Below 55 Years Old:**
- For employees below 55 years old, the total CPF contribution rate is 37%. Out of this, the employee contributes 20%, while the employer contributes 17%. The Ordinary Wage (OW) and Additional Wage (AW) have distinct contribution rates for both employees and employers.
2. **55 to 60 Years Old:**
- The contribution rates are adjusted as individuals enter the age group of 55 to 60. During this period, the employee contribution rate remains at 20%, but the employer contribution rate is reduced to 13%. The adjustment is aimed at gradually shifting the emphasis from accumulation to preparation for retirement.
3. **Above 60 Years Old:**
- Once an individual crosses the age of 60, the CPF contribution rates undergo further adjustments. The employee's contribution remains at 20%, while the employer's contribution decreases to 9%. This reduction reflects the evolving financial priorities as individuals approach their retirement years.
**CPF Contribution Rates for Self-Employed Individuals:**
Self-employed individuals in Singapore are also required to contribute to their CPF accounts. The contribution rates for self-employed individuals differ from those for employees.
1. **Medisave Contribution:**
- Self-employed individuals contribute a percentage of their net trade income to their Medisave accounts, addressing healthcare needs. The Medisave contribution rate is tiered, with higher rates for older individuals.
2. **Special and Retirement Accounts:**
- In addition to Medisave, self-employed individuals contribute to their Special and Retirement Accounts. The rates vary based on age, with a higher percentage allocated to the Retirement Account for individuals aged 55 and above.
**Significance of CPF Contribution Rates:**
Understanding the significance of CPF contribution rates requires a closer look at how these contributions serve as a foundation for financial security and key life milestones.
1. **Retirement Savings:**
- The CPF is a cornerstone of retirement planning in Singapore. The contribution rates are structured to ensure a consistent and gradual accumulation of funds over an individual's working years. As employees progress in age, the allocation to retirement-focused accounts increases, laying the groundwork for a financially secure retirement.
2. **Healthcare Coverage:**
- Medisave contributions play a crucial role in addressing healthcare expenses. The tiered contribution rates for Medisave are designed to accommodate the changing healthcare needs of individuals as they age. This ensures that there are read more adequate funds set aside to cover medical expenses, including hospitalization and outpatient treatments.
3. **Home Ownership:**
- The CPF also supports home ownership through the allocation of funds to the Ordinary Account. Individuals can use their CPF savings to finance the purchase of a home, reducing the financial burden associated with housing loans.
4. **Adaptability to Life Stages:**
- The tiered structure of CPF contribution rates recognizes the evolving financial priorities at different life stages. As individuals progress from their early working years to their retirement years, the allocation of contributions adapts to meet changing needs, fostering financial stability at every stage.
**Implications for Employers:**
CPF contribution rates have implications for employers beyond being a financial obligation. They are intertwined with workforce management, financial planning, and compliance with labor regulations.
1. **Cost of Employment:**
- For employers, CPF contributions represent a significant component of the overall cost of employment. Understanding these contributions is crucial for budgeting and financial planning within organizations.
2. **Workforce Planning:**
- The CPF contribution rates also influence workforce planning. Employers need to consider the financial implications of hiring employees in different age brackets, especially as the contribution rates change with age.
3. **Compliance and Reporting:**
- Ensuring compliance with CPF contribution requirements is a legal obligation for employers. Adhering to the stipulated contribution rates and accurately reporting contributions are essential aspects of labor law compliance.
**Challenges and Considerations:**
While the CPF system is a robust framework for financial security, it is not without challenges and considerations.
1. **Adequacy of Retirement Funds:**
- The adequacy of CPF funds for retirement is a topic of discussion. Some individuals may find the CPF savings insufficient to meet their desired standard of living in retirement. This highlights the importance of personal financial planning and supplementary retirement savings.
2. **Impact of Economic Changes:**
- Economic fluctuations can impact the CPF system. Changes in employment patterns, wage levels, and economic conditions may influence the effectiveness of CPF contributions in meeting the evolving financial needs of individuals.
3. **Flexibility and Withdrawal Policies:**
- The rigidity of CPF withdrawal policies has been a subject of debate. Some individuals may seek greater flexibility in accessing their CPF funds for specific needs, such as education or housing. Balancing the need for flexibility with the long-term goals of the CPF system is a consideration for policymakers.
**Conclusion:**
The CPF contribution rates in Singapore are a fundamental aspect of the nation's social security system, addressing the financial needs of individuals throughout their lives. From retirement savings to healthcare coverage and home ownership, CPF contributions play a pivotal role in shaping financial security and well-being. Understanding the nuances of CPF contribution rates is essential for individuals, employers, and policymakers alike as they collectively navigate the intricacies of financial planning and social security in the dynamic economic landscape of Singapore.